Predicting Interprovincial Rice Food Security in Indonesia as a Pillar of National Defense Using the Random Forest Regressor Algorithm
Keywords:
Food Security, National Defense, Random Forest, RiceAbstract
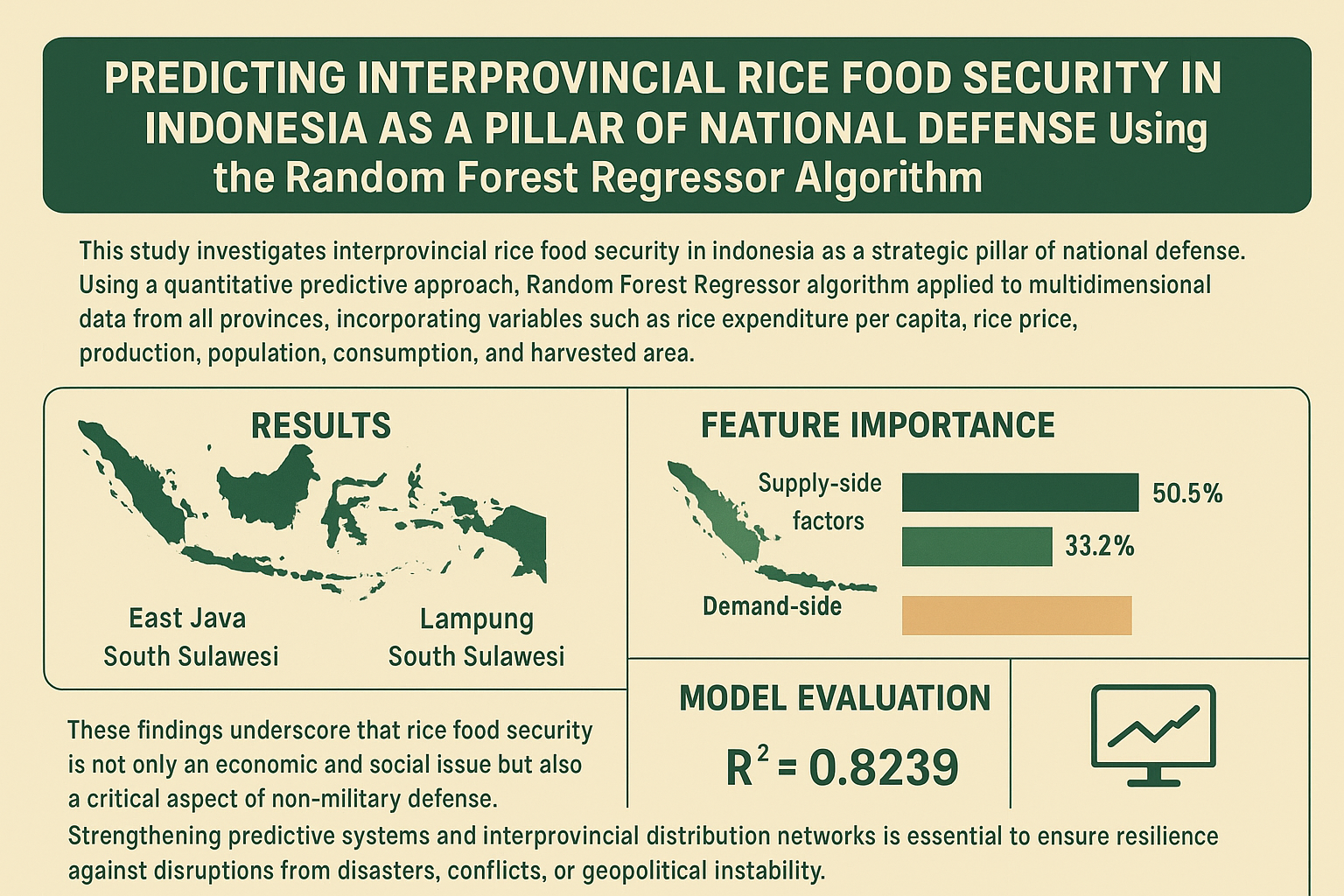
This study investigates interprovincial rice food security in Indonesia as a strategic pillar of national defense. Using a quantitative predictive approach, the Random Forest Regressor algorithm was applied to multidimensional data from all provinces, incorporating variables such as rice expenditure per capita, rice price, production, population, consumption, and harvested area. The results show significant disparities between provinces: surplus regions such as East Java, Lampung, and South Sulawesi contrast sharply with deficit areas like Jakarta, Papua, and Bangka Belitung. Feature importance analysis reveals that supply-side factors, particularly harvested area (50.5%) and production (33.2%), are the most decisive, while demand-side factors have weaker influence. Model evaluation achieved an R² of 0.8239, confirming strong predictive reliability. These findings underscore that rice food security is not only an economic and social issue but also a critical aspect of non-military defense. Strengthening predictive systems and interprovincial distribution networks is essential to ensure resilience against disruptions from disasters, conflicts, or geopolitical instability. The study highlights the practical value of machine learning models in guiding evidence-based policy to secure national food sovereignty.
References
Alifnur Harmawan, R., & Mulyati, E. (2024). Challenges and Strategies for Rice Price Stability: A Systematic Review of Supply Chain Dynamics in Indonesia During Critical Periods. DIVERsITY: FOsTERING UNITY SUsTAINABLE REsEARCH AND INNOVATION SOCIETY, 468–476. https://pns.mypolycc.edu.my/index.php/program/category/139-iric
Allee, A., Lynd, L. R., & Vaze, V. (2021). Cross-national analysis of food security drivers: comparing results based on the Food Insecurity Experience Scale and Global Food Security Index. Food Security, 13(5), 1245–1261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-021-01156-w
Alta, A. (2023). Memodernisasi Pertanian Indonesia. PT. RajaGrafindo Persada-Murai Kencana. https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=KFvTEAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA1&dq=memodernisasi+pertanian+indonesia&ots=FJfIjTx65S&sig=7Ru3Lsedo57Cwq63ZIjeD_xftmw
Atukunda, P., Eide, W. B., Kardel, K. R., Iversen, P. O., & Westerberg, A. C. (2021). Unlocking the potential for achievement of the un sustainable development goal 2 – ‘zero hunger’ – in Africa: Targets, strategies, synergies and challenges. Food and Nutrition Research, 65, 10–29219. https://doi.org/10.29219/fnr.v65.7686
Bakır, R., Orak, C., & Yüksel, A. (2024). Optimizing hydrogen evolution prediction: A unified approach using random forests, lightGBM, and Bagging Regressor ensemble model. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 67, 101–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2024.04.173
Ben Hassen, T., & El Bilali, H. (2022). Impacts of the Russia-Ukraine War on Global Food Security: Towards More Sustainable and Resilient Food Systems? Foods, 11(15), 2301. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152301
BPS. (2025). Produksi Padi dan Beras Menurut Provinsi, 2024.
Chicco, D., Warrens, M. J., & Jurman, G. (2021). The coefficient of determination R-squared is more informative than SMAPE, MAE, MAPE, MSE and RMSE in regression analysis evaluation. PeerJ Computer Science, 7, 1–24. https://doi.org/10.7717/PEERJ-CS.623
Clapp, J., Moseley, W. G., Burlingame, B., & Termine, P. (2022). Viewpoint: The case for a six-dimensional food security framework. Food Policy, 106, 102164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodpol.2021.102164
Cook, A. D. B., & Nair, T. (2021). Non-traditional security in the Asia-pacific: A decade of perspectives. In Non-traditional Security In The Asia-pacific: A Decade Of Perspectives. World Scientific. https://doi.org/10.1142/11941
Fitrawaty, Hermawan, W., Yusuf, M., & Maipita, I. (2023). A simulation of increasing rice price toward the disparity of income distribution: An evidence from Indonesia. Heliyon, 9(3). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13785
Fristin, Y., & Supanto, F. (2021). Development Model of Rice Supply Chain Management to Ensure Self-Sufficiency and Food Security. Jurnal Bisnis Dan Manajemen, 8(2), 353–366. https://doi.org/10.26905/jbm.v8i2.6320
Hidayana, D., Yusgiantoro, P., Midhio, W., Saragih, H. J., & Wijaya, A. R. (2022). Climate Change, Food Insecurity, and National Defense in Archipelago Country: An Interlinked Challenges for Indonesia. Journal of Positive School Psychology, 2022(5), 5412–5424. http://journalppw.com
Hodson, T. O. (2022). Root-mean-square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE): when to use them or not. Geoscientific Model Development, 15(14), 5481–5487. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-15-5481-2022
Larasati, K. K., & Hana, A. (2025). Challenges and Legal Strategies of Indonesia in Global Trade Agreements in the Era of Fragmentation. LIBERATICA, 27(1), 12–22.
Naidu, G., Zuva, T., & Sibanda, E. M. (2023). A Review of Evaluation Metrics in Machine Learning Algorithms. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, 724 LNNS, 15–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-35314-7_2
Pachapur, P. K., Pachapur, V. L., Brar, S. K., Galvez, R., Le Bihan, Y., & Surampalli, R. Y. (2020). Food Security and Sustainability. Sustainability: Fundamentals and Applications, 357–374. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119434016.ch17
Rainio, O., Teuho, J., & Klén, R. (2024). Evaluation metrics and statistical tests for machine learning. Scientific Reports, 14(1), 6086. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-56706-x
Robeson, S. M., & Willmott, C. J. (2023). Decomposition of the mean absolute error (MAE) into systematic and unsystematic components. PLoS ONE, 18(2 February), e0279774. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0279774
Salman, H. A., Kalakech, A., & Steiti, A. (2024). Random Forest Algorithm Overview. Babylonian Journal of Machine Learning, 2024, 69–79. https://doi.org/10.58496/bjml/2024/007
Shanmugasundar, G., Vanitha, M., Čep, R., Kumar, V., Kalita, K., & Ramachandran, M. (2021). A comparative study of linear, random forest and adaboost regressions for modeling non-traditional machining. Processes, 9(11), 2015. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9112015
Tatachar, A. V. (2021). Comparative Assessment of Regression Models Based On Model Evaluation Metrics. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology, 8(9), 853–860. www.irjet.net
Widowati, S., Winarti, C., Hoerudin, & Tjahjohutomo, R. (2024). Recommendations for addressing quality issues of government rice reserve: Indonesia case study. BIO Web of Conferences, 119, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1051/bioconf/202411902009
Yusrin, N. A. (2023). the Analysis of Rice Massive Importing in Indonesia Based on Macroeconomics, Microeconomics, International Economics and Politic Economics. Ultima Management : Jurnal Ilmu Manajemen, 15(2), 308–329. https://doi.org/10.31937/manajemen.v15i2.3411
Zhou, Z., Qiu, C., & Zhang, Y. (2023). A comparative analysis of linear regression, neural networks and random forest regression for predicting air ozone employing soft sensor models. Scientific Reports, 13(1), 22420. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-49899-0