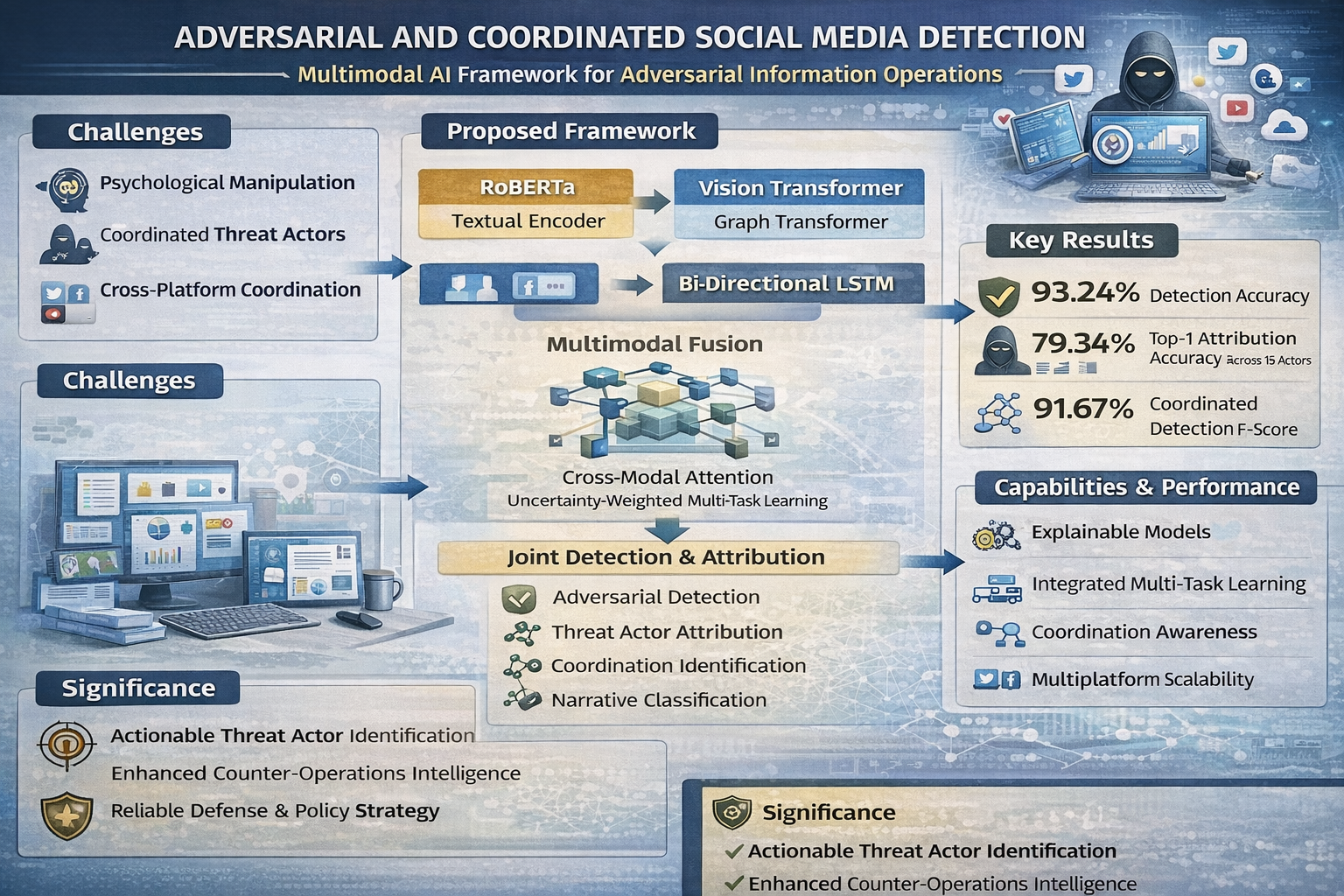
Multimodal deep learning framework for detection and attribution of adversarial information operations on social media platforms
Keywords:
Information Operations, Deep Learning, Multimodal Analysis, Misinformation Detection, Threat AttributionAbstract
Adversarial information operations on social media platforms pose critical threats to national security, with state-sponsored actors exploiting multimodal content manipulation to conduct sophisticated disinformation campaigns. Existing detection approaches focus on single-modality analysis, lacking comprehensive frameworks for simultaneous detection, attribution, and coordination identification. This research develops an integrated multimodal deep learning framework combining RoBERTa-large transformer, Vision Transformer, Graph Convolutional Networks, and bidirectional LSTM, unified through cross-modal attention fusion with multi-task learning optimization. Experimental validation utilizes eight datasets including Russian IRA tweets (3.8M posts), Fakeddit (1M submissions), TweepFake (25K accounts), FakeNewsNet (23K articles), MM-COVID (6.7K posts), CREDBANK (60M tweets), and MEMES (12K items). Results demonstrate 93.24% detection accuracy, 79.34% attribution accuracy across 15 threat actor groups, 91.67% coordination F1-score, 88.62% narrative classification accuracy, and 448ms inference latency suitable for real-time deployment. Ablation studies reveal graph neural networks provide largest performance contribution (5.82% improvement), highlighting social network analysis importance for detecting coordinated behavior. Future directions include large-scale pre-training, adversarial training, continual learning, human-AI collaboration, multilingual expansion, federated learning, and causal inference methods.
References
Alam, F., Cresci, S., Chakraborty, T., Silvestri, F., Dimitrov, D., Martino, G. D. S., Shaar, S., Firooz, H., & Nakov, P. (2022). A survey on multimodal disinformation detection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 45(8), 9442–9464.
Baltrusaitis, T., Ahuja, C., & Morency, L.-P. (2020). Multimodal machine learning: A survey and taxonomy. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 41(2), 423–443.
Bondielli, A., & Marcelloni, F. (2020). A survey on fake news and rumour detection techniques. Information Sciences, 497, 38–55.
Cheng, X., Zhang, H., Xu, Y., & Chen, B. (2021). Image manipulation detection by multi-view multi-scale supervision. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 16, 4235–4247.
Cresci, S. (2020). A decade of social bot detection. Communications of the ACM, 63(10), 72–83.
Dosovitskiy, A., Beyer, L., Kolesnikov, A., Weissenborn, D., Zhai, X., Unterthiner, T., Dehghani, M., Minderer, M., Heigold, G., Gelly, S., & others. (2021). An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. International Conference on Learning Representations.
Giachanou, A., Rosso, P., & Crestani, F. (2022). Multimodal multi-image fake news detection. Journal of Data and Information Quality, 14(2), 1–24.
Jiang, S., Xu, H., Zhang, W., Zhang, L., & Li, Q. (2021). Graph neural networks for social recommendation. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 33(5), 2033–2047.
Keller, F. B., Schoch, D., Stier, S., & Yang, J. (2020). Political astroturfing on Twitter: How to coordinate a disinformation campaign. Political Communication, 37(2), 256–280.
Kendall, A., Gal, Y., & Cipolla, R. (2020). Multi-task learning using uncertainty to weigh losses for scene geometry and semantics. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 7482–7491.
Khan, A., Sohail, A., Zahoora, U., & Qureshi, A. S. (2020). A survey of the recent architectures of deep convolutional neural networks. Artificial Intelligence Review, 53(8), 5455–5516.
Khan, J. A., Saqib, S., Hamza, A., & Arif, Z. (2021). A systematic review on fake news detection using machine learning and deep learning models. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 80, 11413–11447.
Kipf, T. N., & Welling, M. (2020). Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. International Conference on Learning Representations.
Lin, H., Ma, J., Chen, M., Yang, Z., Cheng, X., & Chen, G. (2023). A survey of transformers in fake news detection. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 10(5), 2245–2261.
Linvill, D. L., & Warren, P. L. (2020). Troll factories: Manufacturing specialized disinformation on Twitter. Political Communication, 37(4), 447–467.
Loshchilov, I., & Hutter, F. (2020). Decoupled weight decay regularization. International Conference on Learning Representations.
Lundberg, S. M., Erion, G., Chen, H., DeGrave, A., Prutkin, J. M., Nair, B., Katz, R., Himmelfarb, J., Bansal, N., & Lee, S.-I. (2020). From local explanations to global understanding with explainable AI for trees. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2(1), 56–67.
Madry, A., Makelov, A., Schmidt, L., Tsipras, D., & Vladu, A. (2020). Towards deep learning models resistant to adversarial attacks. International Conference on Learning Representations.
Meel, P., & Vishwakarma, D. K. (2020). Fake news, rumor, information pollution in social media and web: A contemporary survey of state-of-the-arts, challenges and opportunities. Expert Systems with Applications, 153, 112986.
Nakamura, K., Levy, S., & Wang, W. Y. (2020). r/Fakeddit: A new multimodal benchmark dataset for fine-grained fake news detection. Proceedings of the 12th Language Resources and Evaluation Conference, 6149–6157.
Paszke, A., Gross, S., Massa, F., Lerer, A., Bradbury, J., Chanan, G., Killeen, T., Lin, Z., Gimelshein, N., Antiga, L., & others. (2020). PyTorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 32.
Sadeghi, D., Shoeibi, A., Ghassemi, N., Moridian, P., Khadem, A., Alizadehsani, R., Teshnehlab, M., Gorriz, J. M., Khozeimeh, F., Zhang, Y.-D., & others. (2022). An overview of artificial intelligence techniques for diagnosis of Schizophrenia based on magnetic resonance imaging modalities: Methods, challenges, and future works. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 146, 105554.
Sharma, K., Qian, F., Jiang, H., Ruchansky, N., Zhang, M., & Liu, Y. (2022). Combating fake news: A survey on identification and mitigation techniques. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology (TIST), 10(3), 1–42.
Shu, K., Mahudeswaran, D., Wang, S., Lee, D., & Liu, H. (2020). FakeNewsNet: A data repository with news content, social context, and spatiotemporal information for studying fake news on social media. Big Data, 8(3), 171–188.
Tolosana, R., Vera-Rodriguez, R., Fierrez, J., Morales, A., & Ortega-Garcia, J. (2020). Deepfakes and beyond: A survey of face manipulation and fake detection. Information Fusion, 64, 131–148.
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A. N., Kaiser, Ł., & Polosukhin, I. (2020). Attention is all you need. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 30.
Wu, Z., Pan, S., Chen, F., Long, G., Zhang, C., & Philip, S. Y. (2021). A comprehensive survey on graph neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 32(1), 4–24.
Yang, Q., Liu, Y., Chen, T., & Tong, Y. (2020). Federated machine learning: Concept and applications. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology (TIST), 10(2), 1–19.
Zhou, X., & Zafarani, R. (2020). A survey of fake news: Fundamental theories, detection methods, and opportunities. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 53(5), 1–40.
Zhuang, F., Qi, Z., Duan, K., Xi, D., Zhu, Y., Zhu, H., Xiong, H., & He, Q. (2021). A comprehensive survey on transfer learning. Proceedings of the IEEE, 109(1), 43–76.